 |
Welcome To Evlithium Best Store For Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) Battery |
 |
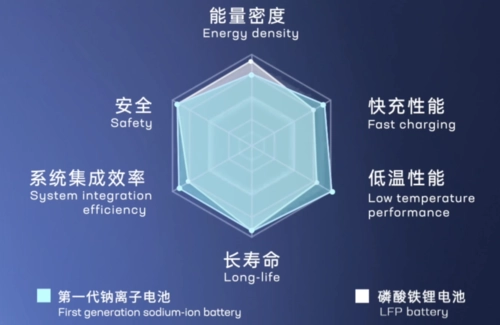
In the pursuit of sustainable and cost-effective energy storage solutions, sodium-ion (Na-ion) batteries are emerging as a formidable alternative to the ubiquitous lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries. Their unique attributes hold promise for transforming the energy storage landscape. Let's delve into the key advantages that position Na-ion batteries as a compelling contender in the realm of energy storage.
One of the most compelling advantages of Na-ion batteries lies in the abundance of sodium, a resource found abundantly in seawater and far more plentiful than lithium. This inherent abundance translates into lower raw material costs, rendering Na-ion batteries a more economically viable option for large-scale energy storage initiatives. With sodium's cost being approximately one-fiftieth that of lithium, the overall production cost of batteries can be significantly reduced, thus making energy storage solutions more accessible to a wider demographic.
The environmental footprint of Na-ion batteries is notably smaller compared to their Li-ion counterparts. The extraction and processing of lithium, often sourced from remote and environmentally sensitive regions, can result in substantial water consumption and ecological degradation. Conversely, sodium extraction from seawater through conventional methods entails a lower carbon footprint and minimal environmental impact. This eco-friendly characteristic aligns seamlessly with the global imperative for sustainable energy solutions.
remains a paramount concern in the battery industry, particularly given the risks associated with thermal runaway and other hazards inherent in Li-ion batteries. Na-ion batteries boast enhanced safety features owing to their chemical composition. They can be discharged to 0V without risking performance degradation, a capability unattainable with Li-ion batteries due to the formation of lithium metal at the anode during discharge to such low voltages. Moreover, sodium's softer chemical nature mitigates the risk of dendrite formation and associated safety hazards during high charging rates.
Na-ion batteries exhibit commendable performance across a broad spectrum of temperatures, rendering them suitable for applications in extreme environmental conditions. Their ability to maintain functionality in both high and low temperatures is particularly advantageous for grid storage applications and electric vehicles operating in diverse climatic settings.
While Na-ion batteries may not supplant Li-ion batteries entirely, they offer a complementary role in the energy storage landscape. In applications where ultra-high energy density is not the primary requisite, such as stationary energy storage and specific electric vehicle applications, Na-ion batteries offer a more sustainable and cost-effective solution. Furthermore, their compatibility with existing Li-ion assembly lines enhances their market viability and potential for widespread adoption.
In conclusion, sodium-ion batteries represent a compelling alternative to lithium-ion batteries, offering a plethora of advantages that position them favorably for future energy storage solutions. As research and development endeavors progress, Na-ion technology is poised to evolve, potentially expanding its applications and diminishing reliance on lithium-based batteries. The horizon of energy storage appears increasingly sodium-rich as the world seeks greener, more economically viable means to power our daily lives.
Edit by editor